Simulation of the behaviour of composite crashworthiness, fatigue resistance and vibroacoustics
The European regulation aims to reduce CO2 emissions to 96 g/km by 2020. To do so, French car manufacturers must reduce vehicle consumption, in particular by reducing structural weight through the use of composites.
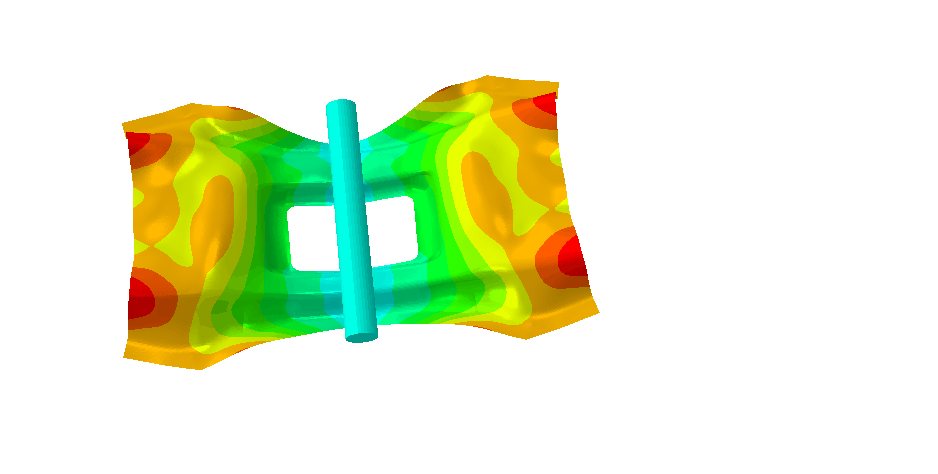
The current softwares do not provide sufficient prediction to integrate composite materials into structural safety parts. A methodological approach to modelling composite materials must therefore be developed in order to improve simulation tools in three areas: crash, fatigue and vibroacoustics.
The COPERSIM project focuses on building a methodological approach to modelling composite materials to improve the simulation tools in three performance areas: crashworthiness, fatigue resistance and vibroacoustics.

Industrial impacts
- Reducing vehicle weight through the use of composites
- Reducing the length of the design phase through the use of more effective tools
Expertise
- Modelling & Simulation
- Composite processes
Partners
- IRT Jules Verne
- ÉCOLE CENTRALE NANTES
- CETIM
- ECN (GeM)
- FAURECIA
- Arts et Métiers Paristech (LEM3)
- PLASTIC OMNIUM
- PSA
- RENAULT
- SOLVAY
- Le Mans Université



